Updated December 2024: Stop error messages and fix your computer problem with this tool. Get it now at this link
Microsoft announced it had fixed a high CPU usage issue affecting some customers running the Diagnostic Policy Service (DiagPS). On October 17th, 2017, we published a blog post titled “Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Services High CPU Usage.” In that post, we described how the Diagnostic Policy Service could use up to 90% of a customer’s CPU resources. We recommended disabling the service if you experienced issues related to high CPU utilization.
The most common causes of high CPU utilization are:
1. A large number of events being logged to Event Logs.
2. An application that uses a lot of memory.
3. A third party product such as Symantec Endpoint Protection or McAfee VirusScan Enterprise.
4. A virus infection.
5. A malicious process attempting to access protected system resources.
Contents
Diagnostic Policy Service is the host of the service High use of CPU
Users are reporting high CPU usage issues related to the Diagnostic Policy Service (DiagPS). This issue occurs when you attempt to run Windows Update while there is an active update process. If you experience this issue, please follow the steps outlined here to resolve it.
If you cannot complete the following steps, please contact Microsoft Support.
Disable the service if none of this works.
Restart your computer.
Run sfc /scannow.
Reboot your computer.
Reinstall the operating system.
We highly recommend that you use this tool for your error. Furthermore, this tool detects and removes common computer errors, protects you from loss of files, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. This software will help you fix your PC problems and prevent others from happening again:
Updated: December 2024
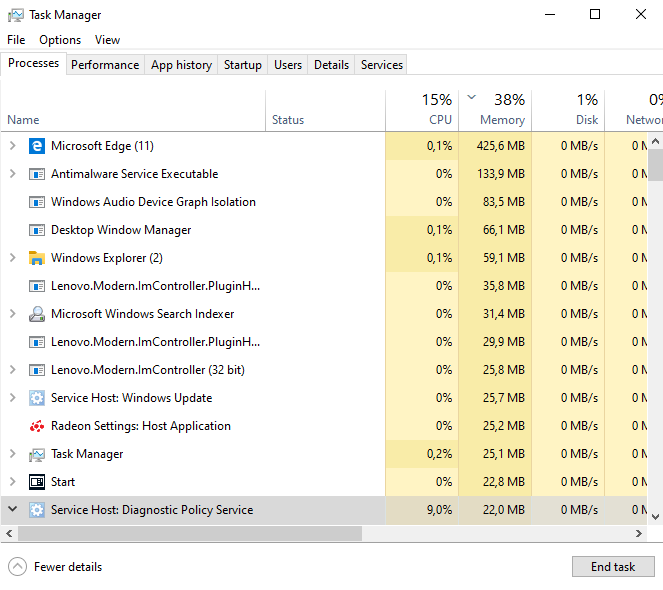
Method 1: Task Manager should stop the process.
To end a process from Task Manage, rightclick on the program name and select End Task from the menu.
When you encounter an error message such as “Windows couldn’t find the file specified”, it usually indicates that something went wrong while trying to open a file. You should check the event log for errors. If you don’t know where to look, just type “eventvwr.msc” into the Start Search box and press Enter.
You’ll find the Windows Error Log under System. Look for events related to the file you’re trying to open.
If you still can’t figure out why a specific file won’t open, you can try reinstalling the software. This way, you’ll avoid having to re-install everything else on your computer.
Method 2: Scanning with SFC and DISM
There are two methods to perform a System File Checker (SFC) scan and a Disk Image Validation (DISM) scan. You can either use the Windows GUI tool or you can do it via command prompt. For example, here is how to run the SFC scan via the GUI:
Type sfc /scannow
Press Enter
Wait for the process to complete. If there are no errors found, you can proceed to the next step.
If you want to run the SFC/DISM scan via command prompt, follow the steps below:
Type sfc –dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
Press enter
You can now close the window.
Method 3: Run the Performance Troubleshooter and make sure Windows is up to date.
If none of the above methods work, try updating Windows and running the Performance Troubleshoot tool. This method could take up to 2 hours depending on how many programs are installed. If you don’t have enough time, you can use the following guide to speed things up.
Open the Start Menu and type “Troubleshooting” into the Search box.
Click on the Troubleshooting option under the search result. You’ll see a list of options. Scroll down till you find the option named “Performance.”
Select it and follow the instructions.
Method 4: Clear the log in the Event Viewer.
The Windows Event Log is a great tool for troubleshooting problems. However, it grows rapidly over time, making it difficult to find specific information about events that occurred months ago. This article describes how you can use one of the most powerful tools in IT—the Command Prompt—to clean up old entries in the Event Viewer.
To clear the Event Viewer logs, follow these simple instructions.
1. Open the Start menu and type cmd into the Search box. Press Enter.
2. In the command prompt window, type the following commands. For example, replace “Administrator” with “Administrator”.
3. When prompted, press Y to confirm each action.
Method 5: Turn off the Diagnostic Policy Service and delete the file SRUDB.dat.
The Diagnostic Policy Service (DiagPSvc) is responsible for providing diagnostic information about Windows devices such as printers, scanners, cameras, etc. When the DiagPSvc runs out of memory, it starts consuming resources like RAM and CPU cycles, causing problems with applications running on the system. If you are experiencing high CPU utilization due to the presence of the DiagPSvc, follow these steps to disable it:
1. Type regedit into the text box and press Enter.
2. Expand HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows Error Reporting\DiagnosticPolicyService. You will see a subkey named CurrentState. Right-click CurrentState and select Delete.
3. Close Registry Editor and reboot the computer.
4. Open Device Manager and look for the following entries:
a. Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
b. Microsoft Data Access Components
RECOMMENATION: Click here for help with Windows errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if the Diagnostic Policy Service in Windows 11 uses a lot of CPU?
If you are facing a high CPU consumption issue while running Microsoft Windows 10, here is what you can try. First of all, open up the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Then locate the process named “Diagnostic Policy Service”. Right-click on it and choose “End Process.” Finally, close the Task Manager window. If the issue persists, you can restart your computer.
What problems show up because Diagnostic Policy Service uses a lot of CPU?
Diagnostic Policy Service consumes a lot of CPU resources. This causes slowdowns in your PC. If you are facing such problems, here is what you need to do.
If you are seeing high CPU usage while playing games, try turning off the Game Bar. You can also disable the Game Bar completely by following the steps given below.
Then uncheck Show the power button on the Start menu.
Step 3: In the Shut Down dialog box, select Restart.
Step 4: Now, just wait till your system restarts.
Step 5: After restarting, open Task Manager. Find the process named Microsoft – Diagnostic Policy Service and end it.
Now, follow the instructions mentioned above again.

