- Download and install the software.
- It will scan your computer for problems.
- The tool will then fix the issues that were found.
Error 0x80042407 appears during system recovery. This happens if the medium was created on computer A and used on computer B (same model as computer A).
In most cases, this problem occurs when users try to use Windows recovery or installation disks to back up a system image to another hard drive or computer with different hardware. If you are one of the victims, you can perform the following troubleshooting steps to resolve the problem.
Contents
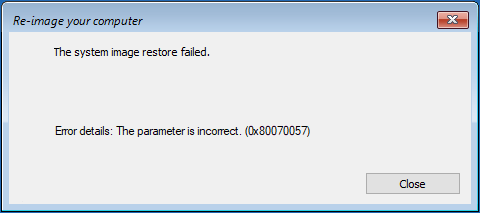
The error looks something like this:
You failed to perform a full recovery of your Windows PC.
Error information: The hard drive installed in BIOS as active is too small to recover the original system hard drive. Replace the hard drive with a larger one and repeat the recovery process. (0x80042407)
Make sure the source and destination computers are using the same mode

In Windows, you cannot restore the system from a UEFI computer to a BIOS computer and vice versa. If the backup was done on a BIOS computer, change the boot mode to Legacy. If the backup was made on a UEFI computer, enable UEFI Boot Mode. To change the firmware mode, start the computer from the Start menu by pressing a specific key during the boot process. You can contact the manufacturer about this. Select UEFI or Legacy from the Start Menu. Thereafter, System Image Restore will no longer fail due to an EFI / BIOS error.
Perform a system restore using the command line
System Restore restores operating system files to an earlier time. System Restore is useful when malware infiltrates your computer and damages system files. Moreover, this feature is important when it comes to ransomware infection options that block computer screens. This guide will guide you through the system recovery process using the command line. In some cases, especially when infected with ransomware, system recovery is challenging because modern fake antivirus and ransomware infections can block Safe Mode and Safe Mode using the network. One solution remains: perform a system restore using the command line.
- Start your computer in safe mode using the command line. When the computer boots up, press the F8 key on your keyboard several times until the Windows Advanced Options menu appears. Then select Safe Mode with Command Prompt from the list and press ENTER.
- When the system boots into command line mode, enter the following line: cd restore and press ENTER.
- Then enter this line: rstrui.exe and press ENTER.
- In the window that opens, click “Next”.
- Select one of the available restore points and click Next (this will restore your computer system to an earlier time and date).
- In the window that opens, click “Yes”.
Updated: January 2025
We highly recommend that you use this tool for your error. Furthermore, this tool detects and removes common computer errors, protects you from loss of files, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. This software will help you fix your PC problems and prevent others from happening again:
- Step 1 : Install PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Step 2 : Click Start Scan to find out what issues are causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click on Repair All to correct all issues.
Make sure the partitions of the source and destination disks are of the same MBR or GPT type.
There are two types of boot modes on computers: legacy BIOS-based and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). In BIOS mode, the system must be installed on an MBR (Master Boot Record) hard disk, and in UEFI mode, on a GPT (GUID Partition Table) hard disk. To recover from a system image recovery due to an EFI / BIOS error, the first thing you need to do is make sure that the source and destination hard disk partitions are of the same MBR or GPT type. Otherwise, you can use DISKPART to convert MBR disk to GPT disk or vice versa.
Run the system file checker.
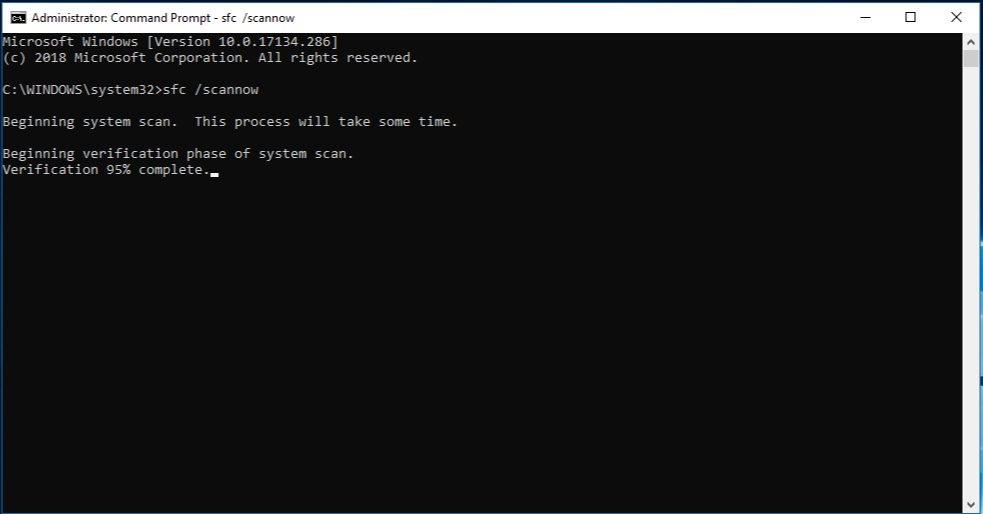
If the problem persists, you can run the System File Checker (SFC) utility. This handy built-in tool will check your file system.
- Press “Start” and type “cmd” on your keyboard.
- cmd should appear in your search results with a black icon.
- Right-click it and select “Run as administrator”.
- If you are prompted for an administrator password, enter the password and click OK.
- A new all-black window will be displayed. You can enter the commands right in this window.
- Type sfc / scannow and press Enter.
- This process will take a long time. You can minimize and modify these black windows.
- After a while go back to the black window and see if the process is complete.
After the SFC process is complete, restart the computer. After restarting, check again for updates.
RECOMMENATION: Click here for help with Windows errors.